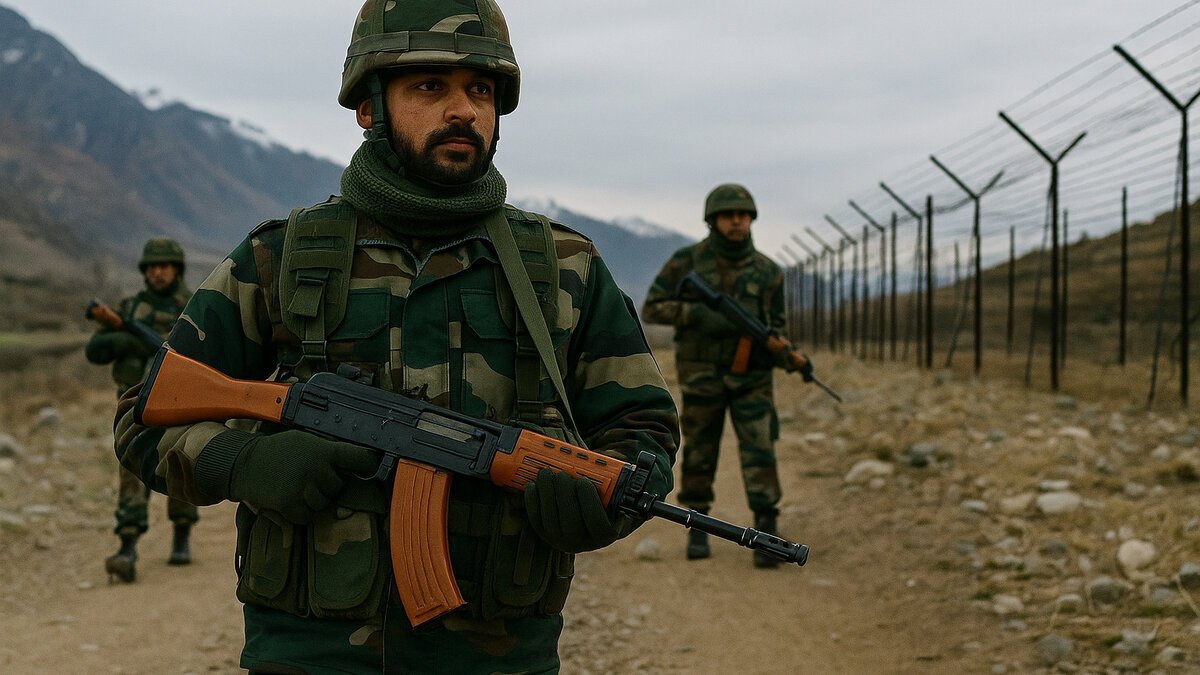
For a country as large and diverse as India, with its long and challenging borders, security is not just a matter of policy — it is the very foundation of national existence. In the face of tensions with Pakistan, China, and other forces that test its borders, the Indian Army must remain vigilant, alert, and well-prepared at every moment.
In this context, the Ministry of Defence’s recent clearance of nearly Rs 2,000 crore worth of emergency procurement is a historic step. It strengthens the armed forces in their counter-terrorism operations, sharpens their precision on the borders, and gives new momentum and technological strength to India’s security forces. It is a strong warning for enemies that India will never compromise when it comes to defending its land and people.
What is Emergency Procurement?
Emergency procurement is a special policy that allows the Indian Army and other security forces to quickly obtain vital weapons, equipment, and technology required for war or crisis situations. Unlike traditional procurement, this process operates under special conditions where urgency is paramount, ensuring that the military can obtain weapons and equipment without delays caused by routine bureaucratic hurdles.
Why and When Did It Begin?
The concept gained prominence after the 2016 Surgical Strikes and the 2019 Balakot Airstrikes. Its real significance became evident during the 2020 Galwan crisis, when tensions with Chinese forces escalated sharply. The Army used the emergency procurement route extensively to obtain advanced weapons and equipment, making a significant difference on the ground. Today, this policy is an integral part of India’s national defense and counter-terrorism framework
The Rs 2,000 Crore Emergency Procurement: An Overview
Recently, the Ministry of Defence cleared nearly Rs 1,981.9 crore worth of 13 emergency procurement projects. This initiative aims to strengthen counter-terrorism efforts, border surveillance, precision attacks, and overall military preparedness.

Key Technologies and Equipment Included:
- Integrated Drone Detection & Interdiction System (IDDIS)
- Low Level Light-Weight Radars (LLLR)
- Very Short Range Air Defence Systems (VSHORADS)
- Remotely Piloted Aerial Vehicles (RPAVs) and Loitering Munitions
- Quick Reaction Fighting Vehicles (QRFVs)
Each of these technologies is critical for boosting the Army’s surveillance, precision, and counter-terrorism capabilities, making it a formidable force for enemies.
Detailed Analysis and Real-World Examples
Integrated Drone Detection & Interdiction System (IDDIS):
This technology can detect, intercept, and neutralize enemy drones.
Where Will It Be Used?
It will be especially valuable in terror-prone areas like Jammu & Kashmir and across the Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC).
Example: Recently, Pakistani drones have been dropping weapons and explosives in Kashmir. IDDIS will help detect and destroy such threats, cutting off terrorist supply lines.
Low Level Light-Weight Radars (LLLR):
These radar systems detect low-flying threats such as helicopters and drones.
Where Will It Be Used?
Ideal for use in mountainous areas like Ladakh and Kashmir, dense forests, and remote border areas.
Example: During the Galwan crisis, LLLR played a crucial role in detecting enemy movements at low altitudes, allowing the Indian Army to respond swiftly and protect its borders effectively.
Very Short Range Air Defence Systems (VSHORADS):
These short-range missile systems can neutralize helicopters, low-flying aircraft, and drones.
Where Will It Be Used?
In forward areas of the LoC and LAC, and for counter-terrorism efforts where precision air defense is vital.
Example: In the tense standoff with Chinese forces in Ladakh (2020), VSHORADS acted as a strong deterrent, providing troops with an effective shield against low-flying enemy aircraft and reconnaissance platforms.
Remotely Piloted Aerial Vehicles (RPAVs) and Loitering Munitions:
These unmanned platforms can locate and strike terrorist targets with precision.
Where Will It Be Used?
Ideal for remote terrains, counter-terrorism operations, and precision attacks where minimal collateral damage is required.
Example: In recent counter-terrorism efforts in Kashmir, RPAVs and loitering munitions have proved highly effective for precision strikes, neutralizing terrorist threats while minimizing the risk to civilians and troops.
Quick Reaction Fighting Vehicles (QRFVs):
These armored vehicles enable rapid response to terrorist attacks and ambushes.
Where Will It Be Used?
Ideal for urban terror hotspots, remote highways, and in providing armored support to troops during counter-terrorism operations.
Example: In Kashmir, QRFVs have been pivotal in responding quickly to terrorist attacks and ensuring the safety of troops and civilians. Similar vehicles can also play a critical role in responding to incidents like the Pulwama attack, providing mobile cover and precision response.

Benefits of Emergency Procurement
- Enables the Army to quickly obtain vital weapons and equipment, making forces more agile and prepared.
- Provides precision and enhanced surveillance for effective border security.
- Supports the “Make in India” initiative by sourcing equipment and technology from domestic firms, boosting the national economy and making India self-reliant.
- Serves as a strong deterrent, sending a message to enemies that any aggression will be met with an effective and immediate response.
The Role of Emergency Procurement in Defence Policy
Emergency procurement occupies a special place in India’s defense policy. By aligning with global standards, it ensures that the Indian Army remains capable of responding quickly to any threat. Its synergy with DRDO and the private sector strengthens national security and promotes “Make in India,” making the Army more resilient and self-reliant.
Modern-Day Examples and Impact of the Policy
- Pulwama Attack (2019): The tragedy acted as a catalyst for utilizing the emergency procurement route, making counter-terrorism efforts stronger and more precise.
- Ladakh Standoff (2020): The Galwan crisis underscored the significance of this policy. Through rapid mobilization and equipment procurement, the Army strengthened its defensive posture and gained a technological edge.
- Jammu & Kashmir Counter-Terrorism Operations: In recent years, equipment sourced through emergency procurement has proved vital for precision strikes and successful counter-terrorism efforts, making the region more secure.
Conclusion and Roadmap for the Future
The Ministry of Defence’s Rs 2,000 crore emergency procurement initiative is more than a policy shift — it is a statement of strength, resilience, and precision. At a time when terrorist threats and border tensions have evolved, this initiative ensures that the Indian Army is not just prepared, but is always one step ahead of its enemies. As “Make in India” and DRDO collaborations gain momentum, this approach will make the Indian Army one of the best-prepared, best-equipped forces in the world. In the years to come, this policy will stand as a beacon of strength for national security — making India a force that no enemy can afford to underestimate.
FAQs
- What is emergency procurement?
It is a special provision allowing the Army to quickly obtain weapons and equipment required in times of crisis, bypassing lengthy bureaucratic delays. - When was this policy introduced?
Although it gained prominence after the 2016 Surgical Strikes and the 2019 Balakot Airstrikes, the policy became especially vital during the Galwan crisis in 2020. - What equipment is included in the Rs 2,000 crore emergency procurement?
Integrated Drone Detection Systems (IDDIS), Low Level Light-Weight Radars (LLLR), Very Short Range Air Defence Systems (VSHORADS), Remotely Piloted Aerial Vehicles (RPAV), Loitering Munitions, and Quick Reaction Fighting Vehicles (QRFVs). - Why is this policy vital for national security?
It allows the Army to quickly obtain critical weapons and equipment required for precision attacks, making it a pivotal part of national security.
AryaLekh (DoFollow) :
- Matcha Shortage: World’s Thirst Dries Up Global Supplies
- Avatar Fire and Ash Full Story and History of the Third Avatar Film – 2025
- Divya Deshmukh Creates History: Wins FIDE Women’s Chess World Cup, Becomes India’s 88th Grandmaster
- Chitrakoot Tourism: Best Places – A Complete Guide to the Spiritual & Natural Wonders of the Ramayana Land 2025
- Asia Cup 2025: UAE to Host the Historic T20 Cricket Showdown from September 9 to 28